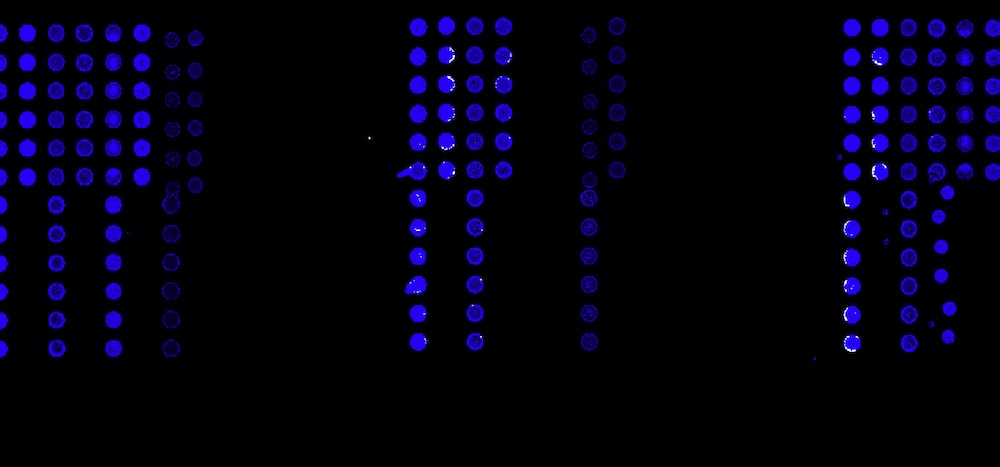
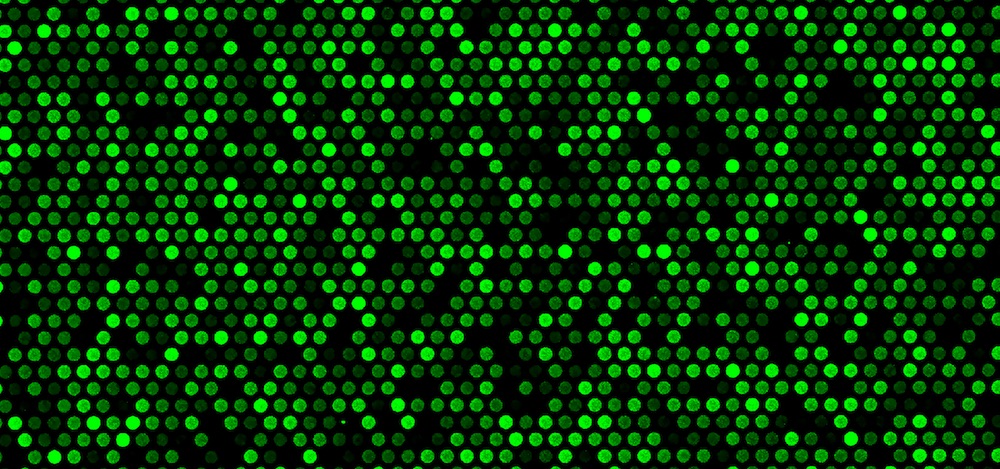
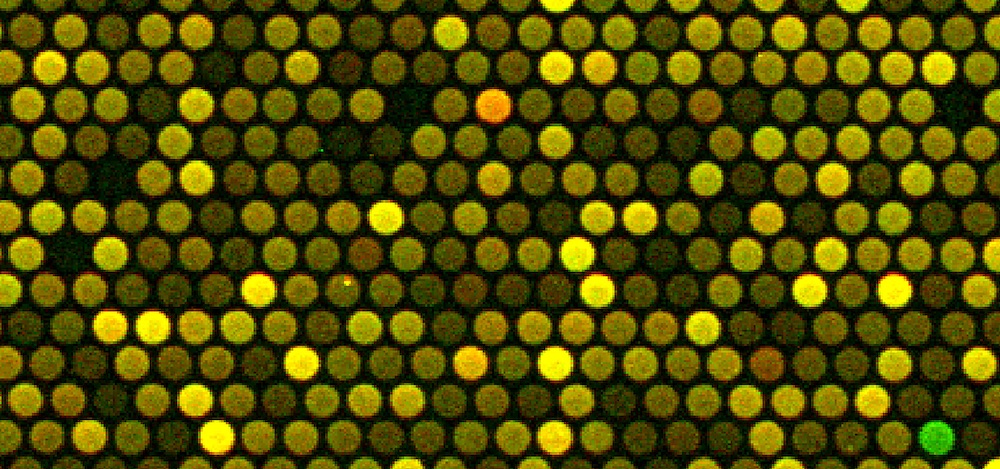
discover our Applications for fluorescence scanners
Select an application for your prefered fluorescence scanner: InnoQuant fluorescence slide scanner, dedicated to tissue imaging or InnoScan microarray scanner, dedicated to microaray studies. Discover our applications for fluorescence scanners.
Complex bacterial vaccines contain multiple components, including protein antigens, lipopolysaccharides, capsule and other macromolecules. Although they are known to provide effective protection against disease, the way in which multiple components combine to elicit a protective response is poorly understood. One way to obtain insight into this important question is by using dedicated protein antigen microarrays.
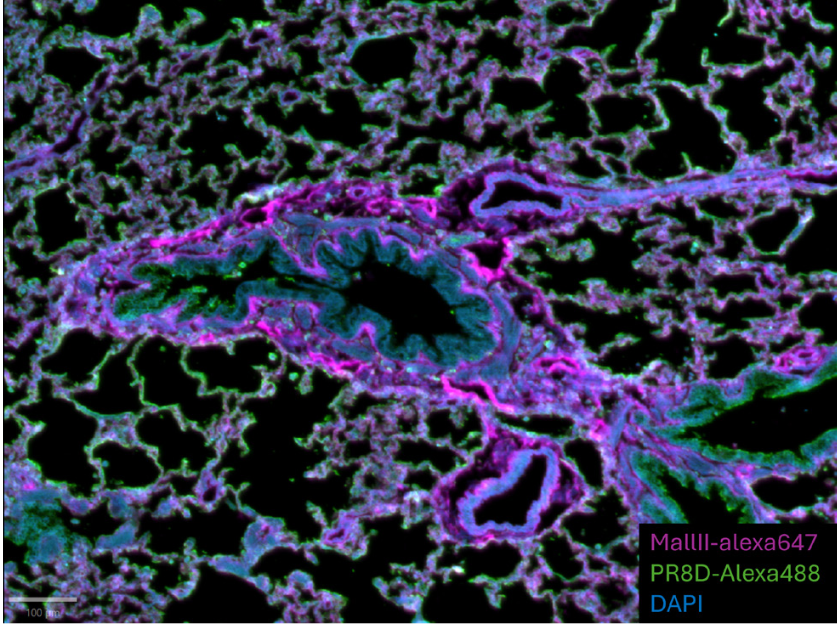
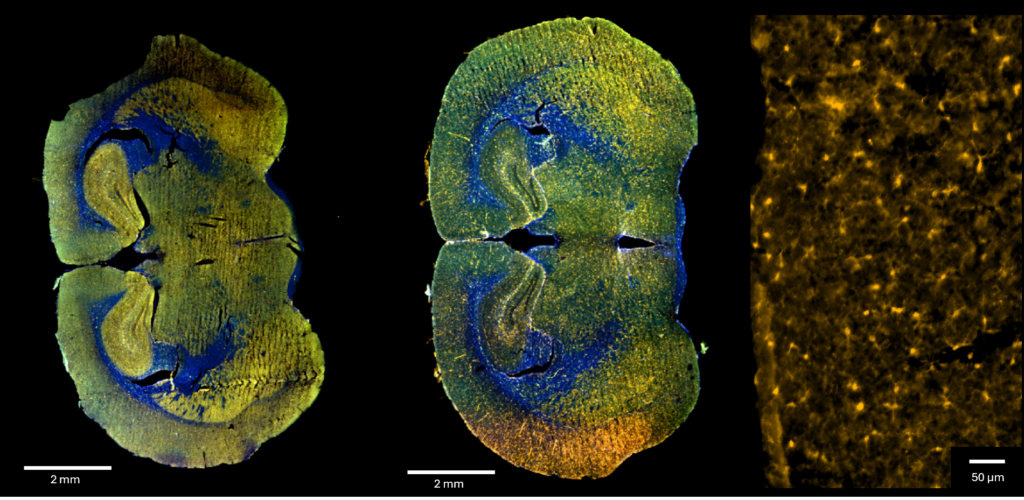
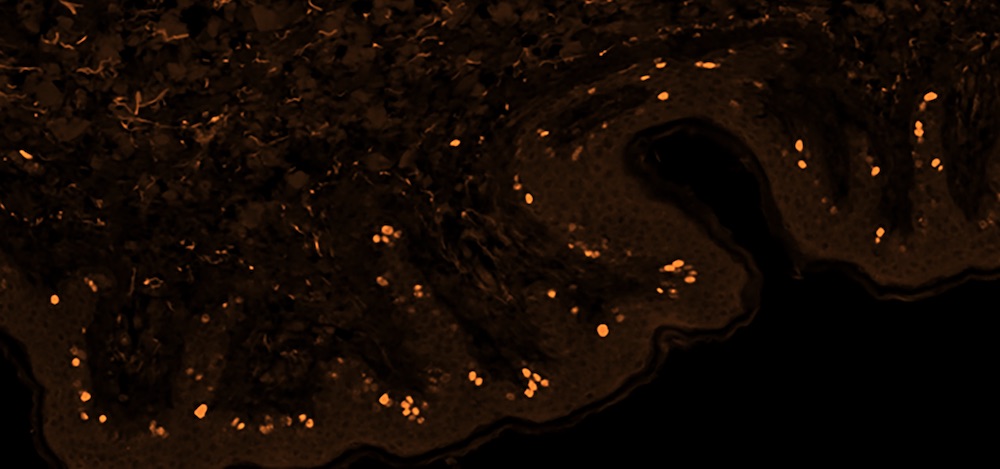
Checking immunofluorescence staining specificity with InnoQuant scanner for studying the display of sialic acid in large ferret lung tissue sections
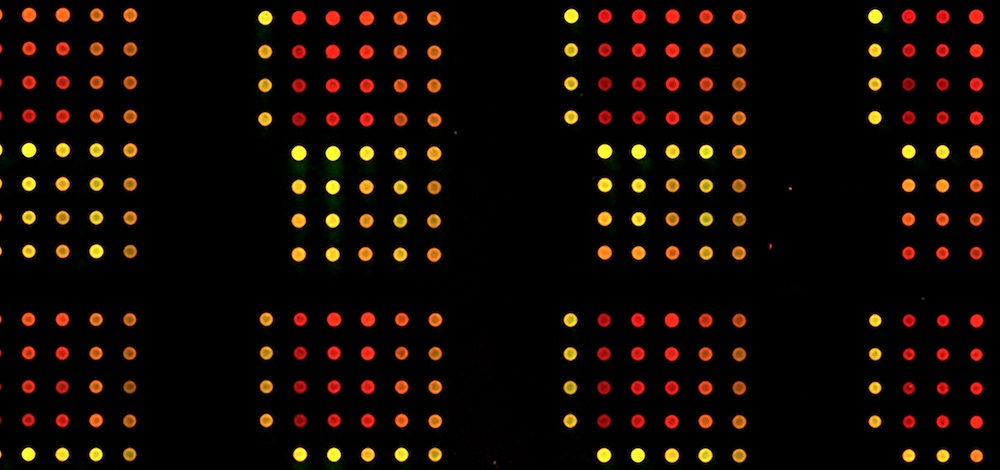
Reverse Phase Protein Arrays (RPPAs) are increasingly used to study cell signaling as they are highly multiplexed and allow precise quantification of protein of interests in biological samples.
Reverse Phase Protein Arrays (RPPAs) are a specific type of protein arrays consisting of printed cell lysates useful for cell signaling and biomarker analysis. RPPAs are mainly built on nitrocellulose film slides as they have high binding capacity and viability for native proteins.
Protein microarrays are the template of choice for many diagnostic applications and proteomic analyses. Reverse Phase Protein Arrays (RPPA) enable the protein content analysis of hundreds of samples in a single assay. Furthermore, picoliter amounts of samples are most often sufficient to provide a significant signal for a given factor.
InnoScan 710- IR when coupled with pGOLD slides from Nirmidas Biotech, is able to quantify cytokine levels over the relevant 6 logs of dynamic rage thanks to the near-infrared detection of the InnoScan 710-IR scanner and the metal- enhanced fluorescence (MEF) capabilities of the pGOLD slides.
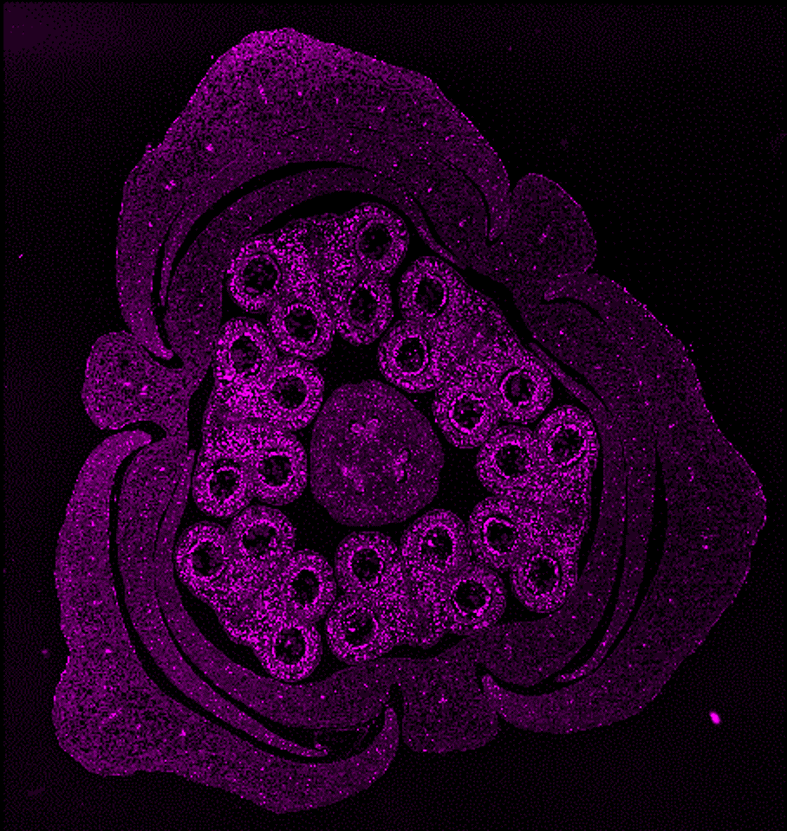
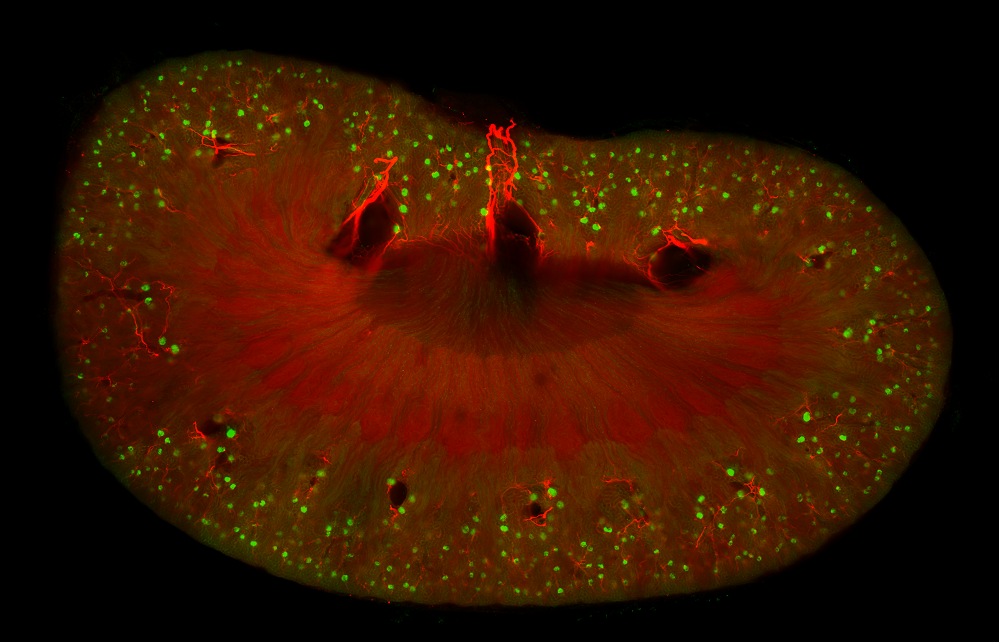
The study of plant tissues through fluorescence imaging is becoming increasingly essential in plant biology, biotechnology, and agronomy. To properly investigate these specimens, the use of a slide scanner, originally developed for histology or cytology, proves to be a valuable tool, offering both high-resolution imaging and large field acquisition capabilities.
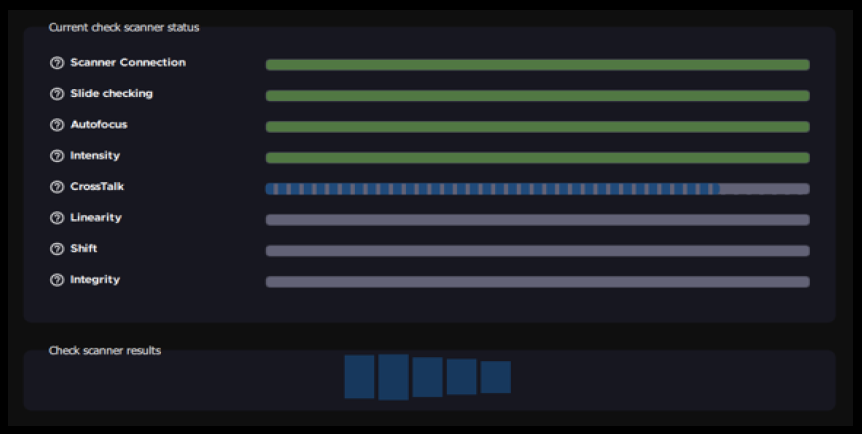
Ensuring reproducible and reliable results for fluorescence imaging with the tailored Argolight slide and InnoQuant's unique optical design.
Aadvancements in imaging technology have introduced slide scanners, which allow users to image multiple samples in a single session with minimal user input, enabling more efficient project scaling.
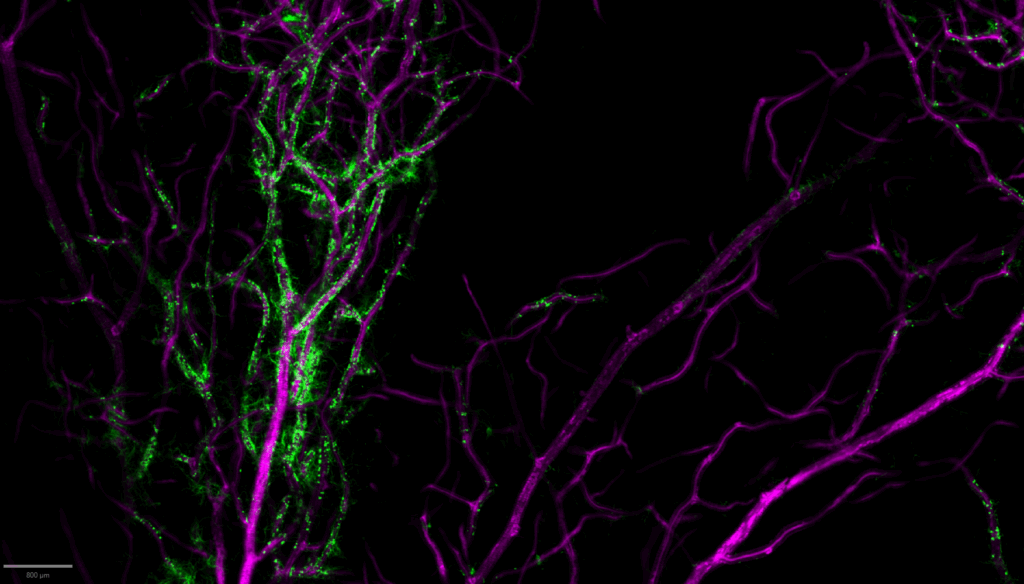
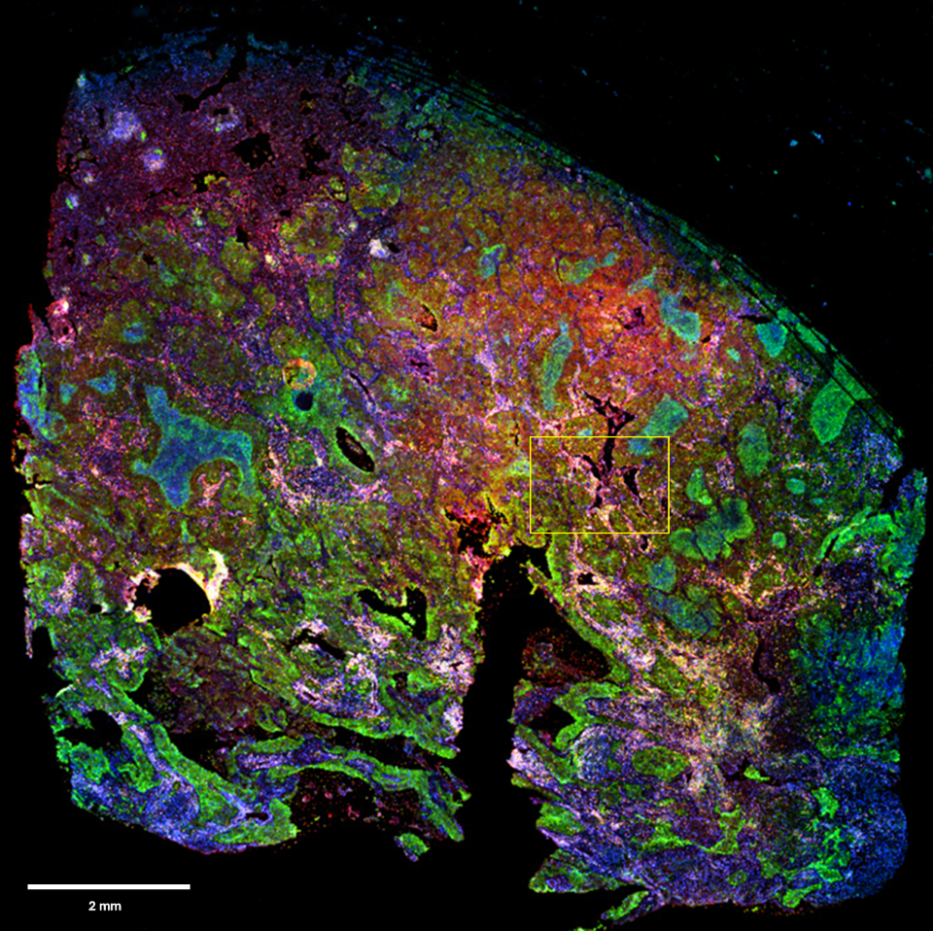
In the field of cancer research, many advancements have been made over the last decade through studies of the tumor microenvironment. Tumor sample tissues are characterised by a significant spatial heterogeneity associated with biological complexity.
Plants are ideal organisms in the studying of cell functions and organization. In comparison to an animal model, plants are easy to growth and manipulate.
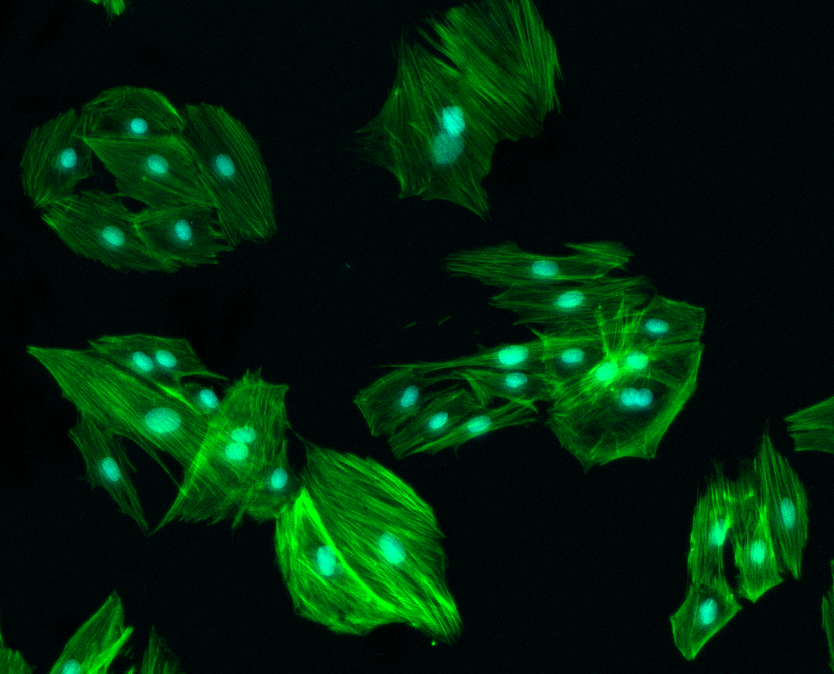
Fluorescence immunostaining techniques on cultured cells or individual cells help to follow the protein expression and activity changes by targeting specific antigens with fluorescence-labelled antibodies.
Using fluorescence-labelled antibodies against specific antigens make it possible to highlight the presence of a molecule of interest directly within a tissue section.
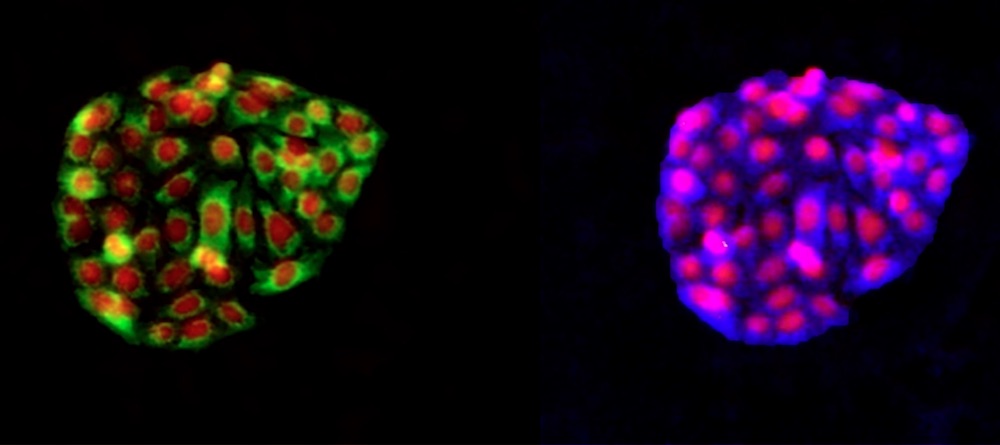
Using Cell Microarray (CMAs) it is possible to study the interactions and behaviors of cells face to different stimuli. CMAs can be created by spotting different cell binding molecules such as extracellular matrix proteins.
Viruses, bacteria and parasites can cause deleterious diseases requiring rapid and efficient detection and therapeutic tools. Emerging infectious diseases with little known mechanisms of infection and pathogenicity represent a big challenge for research and clinics.
Protein detection by fluorescence-labelled antibodies on tissue sections is a widely used technique for the biomarker screening in complex diseases such as cancer to define biomarker expression on tumor cells and its distribution on a defined tissue.
Reverse Phase Protein Arrays (RPPA), also named cell lysate arrays, have been shown to be a useful tool for biomarker evaluation in large patient cohorts.
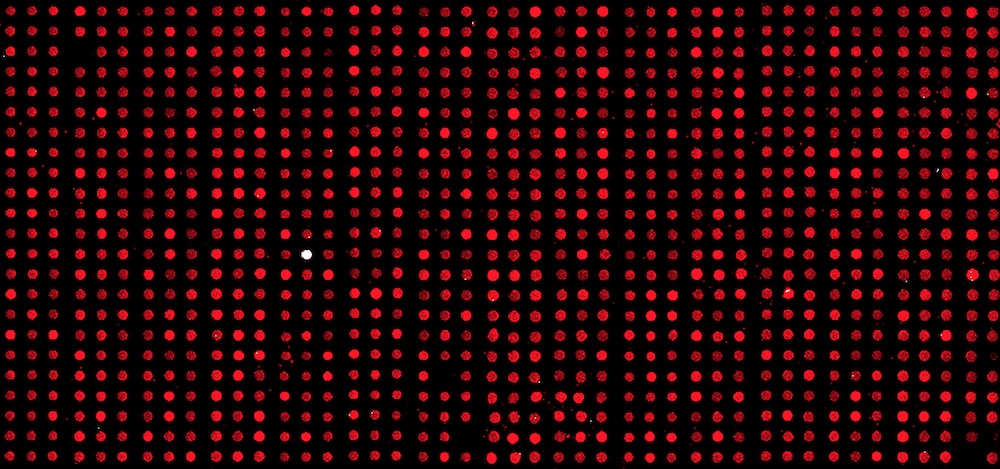
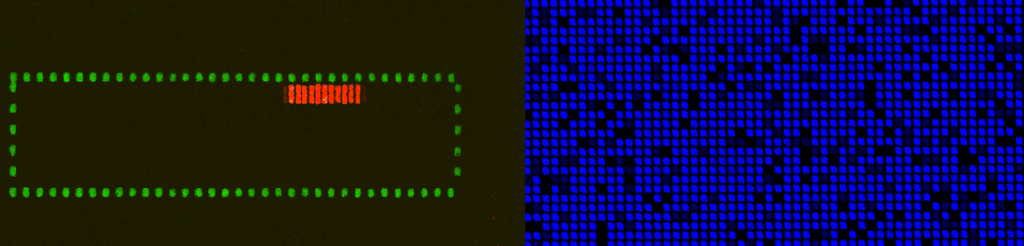
Genes are transcribed into messenger RNAs which represent the dynamic and biologic state of a cell at a given time. Using DNA microarrays, it is possible to identify mRNAs present in a sample and quantify their levels
Protein arrays are widely used in labs in order to study protein functions and interactions involved in different cell processes. For example, kinase arrays allow the study of the activity of protein kinase.
Array CGH (aCGH) analysis to determine chromosomal Copy Number Variation (CNV) is nowadays a routine laboratory technique on cytogenetics research and diagnostics.
Proteins are considered to be the key effectors of cellular response to external stimuli. Differential expression of key proteins can modulate cell fate, either cell differentiation, proliferation or death. Protein microarrays are a powerful tool for high-throughput screening